Apple Pay
Available in dozens of countries around the world in participating retail stores, apps, and websites.

Apple Pay Overview
Contents
Apple Pay is Apple's mobile payments service that initially launched in 2014. It is designed to allow iPhone, iPad, Mac, and Apple Watch users across the world to make payments for goods and services directly with credit and debit cards stored in their devices.
Apple Pay also lets users make one-tap purchases within apps that have adopted the Apple Pay API and on the web, with this functionality available to iPhones, iPads, and Macs with Touch ID or Face ID and NFC. Apple devices use a "Secure Element" for Apple Pay, keeping customer information secure and private.
Apple offers person-to-person Apple Pay payments through the Messages app on the iPhone and Apple Watch, plus there are also in-person payment options with iOS 18. Using Apple Cash, you can send money to friends or family in the United States. Apple also introduced its own credit card, the Apple Card, which has unique perks and benefits and offers deep integration with Apple Pay and the Wallet app.
To keep transactions secure, Apple uses a method known as "tokenization," preventing actual credit card numbers from being sent over the air. Apple also secures payments using Touch ID or Face ID on compatible iPhones and continual skin contact on the Apple Watch.
Apple is aiming to replace the wallet with Apple Pay, and the one-step payment process prevents people from needing to dig through a purse or wallet to find credit or debit cards. Because it is built on existing NFC technology, Apple Pay works anywhere NFC-based contactless payments are accepted, plus it is available on the web for online purchases.

Apple Pay is the most popular mobile payment platform in the United States, and it is on track to account for 10 percent of global card transactions by 2025. Since 2014, Apple has expanded Apple Pay to dozens of countries.
Note: See an error in this roundup or want to offer feedback? Send us an email here.
Setting Up Apple Pay
Apple Pay can be set up in the Wallet app. Tapping the "+" icon in Wallet lets users to add a credit or debit card to Apple Pay, either selecting a card already on file with iTunes or scanning one in with the camera. Apple Pay can also be set up by using the prompts when setting up a new iPhone, iPad, or Mac.
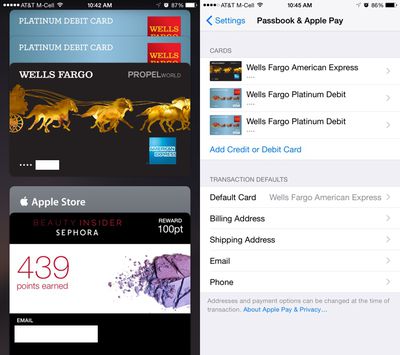
Credit and debit cards are verified in just a few seconds, but some cards require a phone call, app download, or an email to verify a card before it can be added to Apple Pay. Once a card is verified, it is immediately available for purchases both in stores and within apps. Up to eight cards can be registered with Apple Pay at one time.
Apple Pay can be managed in the Settings app, located in the "Wallet and Apple Pay" section. Each card added to Wallet is listed in that section, along with information like billing address, email, and phone number. Tapping on a card offers specific information like last digits of the card number, last digits of the Device Account Number that replaces the card number in transactions, and it also provides contact information for the bank that issued the card.
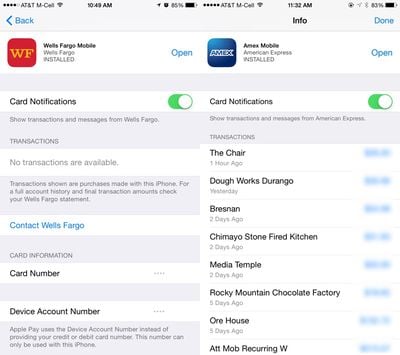
Some cards are also able to display transaction information, offering a list of recent transactions that have been made, with Apple Pay or with a traditional purchase via physical card.
Apple Pay How Tos
How It Works
In a retail store, when approaching a point-of-sale system compatible with Apple Pay, the screen of the iPhone lights up and opens Wallet automatically, where a user can tap on a credit card to be used or pay with the default Apple Pay card.
A payment is made by holding a compatible iPhone or Apple Watch near a checkout system that includes NFC, most of which look like standard card checkout terminals within stores. A completed payment is denoted by a slight vibration, a check mark on the screen, and a beep. On devices with Face ID, a facial scan is used for authentication, and on devices with Touch ID, a fingerprint scan is required.
In some stores and in some countries, users may still be asked for a PIN code due to older point-of-sale machines, transaction limitations, and laws in certain countries, but for the most part, checking out with Apple Pay is an easy one-step process that does not require a signature or PIN.
With Apple Pay, a cashier does not see a credit card number, a name, an address, or any other personally identifying information, making it more secure than traditional payment methods. There is no need to take out a credit card or confirm the authenticity of a credit card with a driver's license or ID card, because all of that information is stored on the iPhone and protected by several built-in security systems, including Touch ID and Face ID.
Making a payment online via Apple Pay is just as simple as an in store payment because it uses the same credit card and authenticates with Touch ID or Face ID in participating apps that have adopted the Apple Pay API. Using Apple Pay in an app or on a website bypasses all of the steps that are usually required when making an online purchase, including entering shipping and payment information.
After an item is added to an online cart and a user initiates the checkout process, Apple Pay can be selected as the payment method. The shipping/billing address associated with the credit or debit card on file is automatically entered, as is a user's name, and the purchase is confirmed via Touch ID or Face ID. During this process, information like shipping address can be altered, which is useful when ordering a gift. Online payments using Apple Pay for the web follow the same process.
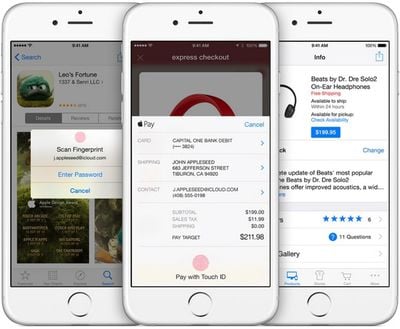
Online and retail store payments are both limited to participating merchants. Apple Pay is only available within apps and on websites that have adopted the Apple Pay API and to make a payment in a retail location, the shop needs to support Apple Pay directly or allow NFC payments. As of iOS 18, Apple Pay can be used with third-party browsers, even on PCs.
In More Detail
Compatible Devices
Apple Pay in stores is available for the iPhone 6 and later, including all modern iPhone models. All of Apple's iPhones after the iPhone 6 include near-field communication (NFC) chips. Apple Pay also works with Apple Watch, the company's wrist-worn wearable device, plus it can be used with Macs and iPads that support Touch ID or Face ID. On non-compatible Macs, a connected iPhone can be used for authentication.
Security
Apple puts a heavy emphasis on security when advertising Apple Pay, to assure iPhone owners that their payment information is safe, and, in fact, safer on an iPhone than inside of a wallet. According to former credit card executive Tom Noyes, the way Apple Pay has been designed to work makes it "the most secure payments scheme on the planet."
When a credit or debit card is scanned into Wallet for use with Apple Pay, it is assigned a unique Device Account Number, or "token," which is stored in the phone rather than an actual card number.
The iPhone itself has a special dedicated chip called a Secure Element that contains all of a user's payment information, and credit card numbers and data are never uploaded to iCloud or Apple's servers. When a transaction is made, the Device Account Number is sent via NFC, along with a dynamic security code unique to each transaction, both of which are used to verify a successful payment. The dynamic security code is a one-time use cryptogram that replaces the credit card's CCV and is used to ensure that a transaction is being conducted from the device containing the Device Account Number.
Dynamic security codes and Device Account Numbers (aka, tokens and cryptograms) are not unique to Apple and are built into the NFC specification that the company is adopting. In fact, much of the Apple Pay system is built on existing technology.
Along with Device Account Numbers and dynamic security codes, Apple also authenticates each transaction through Touch ID or Face ID. Whenever a transaction is conducted with an iPhone, a user must place a finger on Touch ID or complete a facial scan for the payment to go through.
With the Apple Watch, authentication is done through skin contact. When the watch is placed on the wrist, a user is prompted to enter their passcode. After a passcode is entered, as long as the device continues to have contact with the skin (which is monitored through the heart rate sensor), it's be able to be used to make payments. If the watch is removed and skin contact is lost, it can no longer be used to make payments.
Both Touch ID, Face ID, and the skin contact authentication method in the Apple Watch prevent someone who has stolen an iPhone or Apple Watch from making an unauthorized payment.
Because Apple utilizes Device Account Numbers, a user's credit card number is never shared with merchants or transmitted with payments. Store clerks and employees do not see a user's credit card at any point, and they also do not have access to personal information like a name or address because an ID is not required for verification purposes.
Furthermore, if an iPhone is lost, the owner can utilize the Find My app to suspend all payments from the device, without needing to go through the hassle of canceling credit cards.
Banks are confident in Apple Pay's security, and have opted to assume liability for any fraudulent purchases made both in retail stores and online using the system.
Privacy
Apple has been careful to point out the company does not store or monitor the transactions that people make with Apple Pay. Apple says it does not know what people are purchasing, nor does it save transaction information.
"We are not in the business of collecting your data," said Eddy Cue during the keynote speech introducing Apple Pay. "Apple doesn't know what you bought, where you bought it, or how much you paid. The transaction is between you, the merchant, and the bank."
U.S. Partners
Compatible Credit Cards and Banks
Apple has partnered with the major credit and debit card companies in the United States: Visa, MasterCard, Discover, and American Express. Apple has also signed deals with all major banks, including Bank of America, HSBC, Capital One, Chase, Citi, American Express, and Wells Fargo, plus it has established deals with hundreds of smaller banks across the country.
Apple Pay is compatible with a number of in-store credit cards from companies that include Kohl's, JC Penney, and BJ's, and some cards also let customers earn rewards.
A current list of partners can be found on Apple's participating banks support document.
Retail Partners:
Because Apple Pay is based on already existing NFC technology, the service works in hundreds of thousands of locations that accept contactless payments in the countries where Apple Pay is accepted. Apple Pay is accepted in more than a million retail stores, restaurants, gas stations, grocery stores, and more across the United States.
Some of Apple's partners include Best Buy, B&H Photo, Bloomingdales, Chevron, Disney, Dunkin Donuts, GameStop, Jamba Juice, Kohl's, Lucky, McDonald's, Office Depot, Petco, Sprouts, Staples, KFC, Trader Joe's, Walgreens, Safeway, Costco, Whole Foods, CVS, Target, Publix, Taco Bell, and 7-11.
Transit systems in Philadelphia, Portland, Chicago, New York, Boston, San Diego, Los Angeles, Hong Kong, Toronto, Montreal, Toronto, Washington, D.C., San Francisco, and 275 cities in China have added support for Apple Pay, with a list of states, countries, and regions that support Apple Pay for transit available here.
Apple Pay can be used to pay for transit on iPhone and Apple Watch, and in many of the above listed areas, Express Transit Mode is available. With Express Transit Mode, the iPhone and Apple Watch can be used to quickly pay for rides without having to unlock the device, open an app, or validate with Face ID/Touch ID.
Apple Pay is also available in many places outside of traditional retail stores, including universities, ballparks, non-profit organizations, Bitcoin payment providers, and even ATMs from Bank of America, Chase, and Wells Fargo.
A full list of locations where Apple Pay is accepted in the United States can be found on Apple's Apple Pay website.
Apps:
Apple Pay support can be built into any app, and thousands of apps, representing businesses both big and small, accept Apple Pay as a payment method in their apps. When used in an app, Apple Pay payments can be made on iPhones and iPads equipped with Touch ID or Face ID.
Apple Pay Loyalty Card Integration
In the fall of 2015, Apple Pay began working with various store loyalty programs, allowing customers with loyalty cards stored in the Wallet app to use them over NFC in participating stores. Loyalty cards from eligible stores added to Wallet pop up at NFC terminals just like credit cards.
Walgreens was the first company to support the Apple Pay loyalty program. Walgreens customers can add their Walgreens rewards cards to Wallet where they can be used like any other credit or debit card during the checkout process to earn rewards points.
Checking out with a rewards card is a two-step process in most stores -- first it's necessary to activate the rewards card with a finger on Touch ID, followed by the actual payment. Kohl's is an exception, having introduced one-touch rewards and payment integration.
Apple's Cut
Apple collects a fee from banks each time consumers use the Apple Pay payment solution to make a purchase. According to rumors, Apple has struck individual deals with each bank it has partnered with, including Chase, Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and more.
Apple's cut is reportedly at approximately 0.15 percent of each purchase, which equates to 15 cents out of each $100 purchase.
Apple Pay on the Web
Apple Pay is also available on the web, with the payments service offered on participating websites when checking out. Many websites and payment providers like Stripe, WePay, and SquareSpace support Apple Pay on the web.
On Macs with a fingerprint sensor, purchases are verified through Touch ID. On other machines, purchases are verified through a connection to an Apple Watch or an iPhone, with the purchase authorized via Touch ID/Face ID, and on the iPhone and iPad, purchases are authorized through Touch ID or Face ID as normal.
Apple Cash
Apple Cash is a peer-to-peer payment option designed to allow users to send money via Apple Pay using Messages on the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch. Apple Cash lets you send money to friends and family with a connected debit card, similar to services like Square Cash or Venmo.
Money can be sent in Messages using standard fingerprint/face authentication (or skin authentication on the Apple Watch), and funds received are available in a new Apple Cash card that's located in Wallet. This card can be used to make Apple Pay purchases where Apple Pay is accepted (similar to any other credit or debit card stored in Apple Pay), or it can be transferred to a bank account. Apple partnered with prepaid card provider Green Dot for the Apple Cash card.

Like many peer-to-peer money transferring services, sending money is free when a debit card is used, and while Apple used to allow money to be loaded using a credit card for a small fee, you can now only add money to Apple Cash via a debit card. Apple Cash is limited to the United States.
As of iOS 18, there is a Tap to Cash feature that allows Apple Cash to be exchanged in person by tapping two iPhones or Apple Watches together. Sending money this way does not require knowing the other person's phone number or email, making it ideal for quick in-person purchases.

The Apple Card
Apple in August 2019 introduced the Apple Card, its own credit card in partnership with Goldman Sachs and Mastercard. The Apple Card is a physical and digital credit card that iPhone users in the U.S. can sign up for on the iPhone.

Apple Card works like a traditional credit card, but it is deeply integrated into the Wallet app, offering up real-time views of the latest transactions and a complete overview of spending organized by category along with payment options optimized for encouraging minimal interest.
Apple has a "Daily Cash" cash back program that gives you 1 percent cash back on all purchases, 2 percent cash back on all Apple Pay purchases made with Apple Card, and 3 percent on all Apple-related purchases at Apple retail stores, the App Store, iTunes, and some third-party partner stores. Daily Cash is immediately available in the Wallet app, delivered on the Apple Cash card.
Apple also offers three percent cash back when using the Apple Card with Apple Pay for Uber, Uber Eats, T-Mobile, Walgreens, Nike, and Duane Reade purchases. In the future, Apple also plans to bring three percent cash back rewards to other merchants and apps.
Customer support for Apple Card is done through the Messages app, and there are no fees associated with the card. Apple is aiming to provide low interest rates, but APR is be based on credit score and credit approval is required. Privacy is a major focus, and the physical Apple Card - made out of titanium engraved with your name - has no number on it, no signature, and no expiration date, with info instead stored in the Wallet app.
We have a full guide with everything that you need to know about Apple Card available here.
Tap to Pay on iPhone
Apple in February 2022 introduced "Tap to Pay on iPhone," a feature designed to allow NFC-compatible iPhones to accept payments through Apple Pay, contactless credit and debit cards, and other digital wallets, without requiring additional hardware.

Tap to Pay works with the iPhone XS or later, allowing supported iOS apps to accept iPhone to iPhone payments. At checkout, a merchant is able to prompt a customer to hold their iPhone, Apple Watch, contactless credit or debit card, or other digital wallet close to the merchant's iPhone to complete a payment over NFC. Note that Tap to Pay is separate from Tap to Cash, an iPhone-to-iPhone payment option that uses Apple Cash.
International Expansion
Apple began expanding Apple Pay outside of the United States in 2015, launching the payment service in the UK, Australia, and Canada. From there, it expanded to dozens of other countries. Apple today is still working to expand Apple Pay worldwide, as it is not available in some major countries like India.
Apple Pay can be used with supported debit and credit cards in Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Belarus, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, China, Colombia, Costa Rica, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, El Salvador, Estonia, Faroe Islands, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Greenland, Guernsey, Guatemala, Honduras, Hong Kong, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Isle of Man, Israel, Italy, Japan, Jersey, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macao, Malaysia, Malta, Mexico, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, Morocco, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Palestine, Panama, Peru, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, San Marino, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, The United States, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, Vatican City, and Vietnam.
More information on availability and participating financial institutions in each country or region can be found on Apple's website.
NFC in Europe
While Apple Pay is the only payment method that is able to access the NFC chip in the iPhone for tap-to-pay capabilities, that is changing with the launch of iOS 17.4. The update allows third-party payment providers and banks to use the NFC chip in countries located in the European Economic Area.
That means alternative payment options can be set as the default that will activate when an iPhone is placed near a contactless payment terminal.
Competition
Walmart, the biggest retailer in the United States has refused to implement Apple Pay and has instead rolled out its own proprietary payment system, Walmart Pay. With Walmart Pay, customers can make purchases and payments in Walmart retail locations using a QR code in the Walmart app. Walmart Pay is available nationwide at all Walmart locations.
Other Apple Pay competitors include Samsung Pay and Google Pay (formerly known as Android Pay), two mobile payment solutions created by Samsung and Google, respectively. These payment solutions are largely designed for Android devices, but even iPhone users can use Google Pay Send for sending money to friends.

